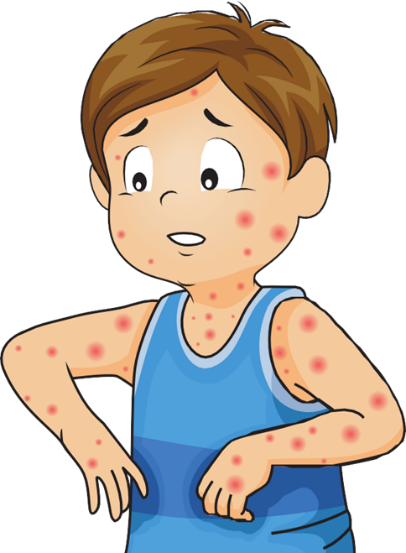
Chickenpox usually begins with:
- Fever
- Tiredness
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
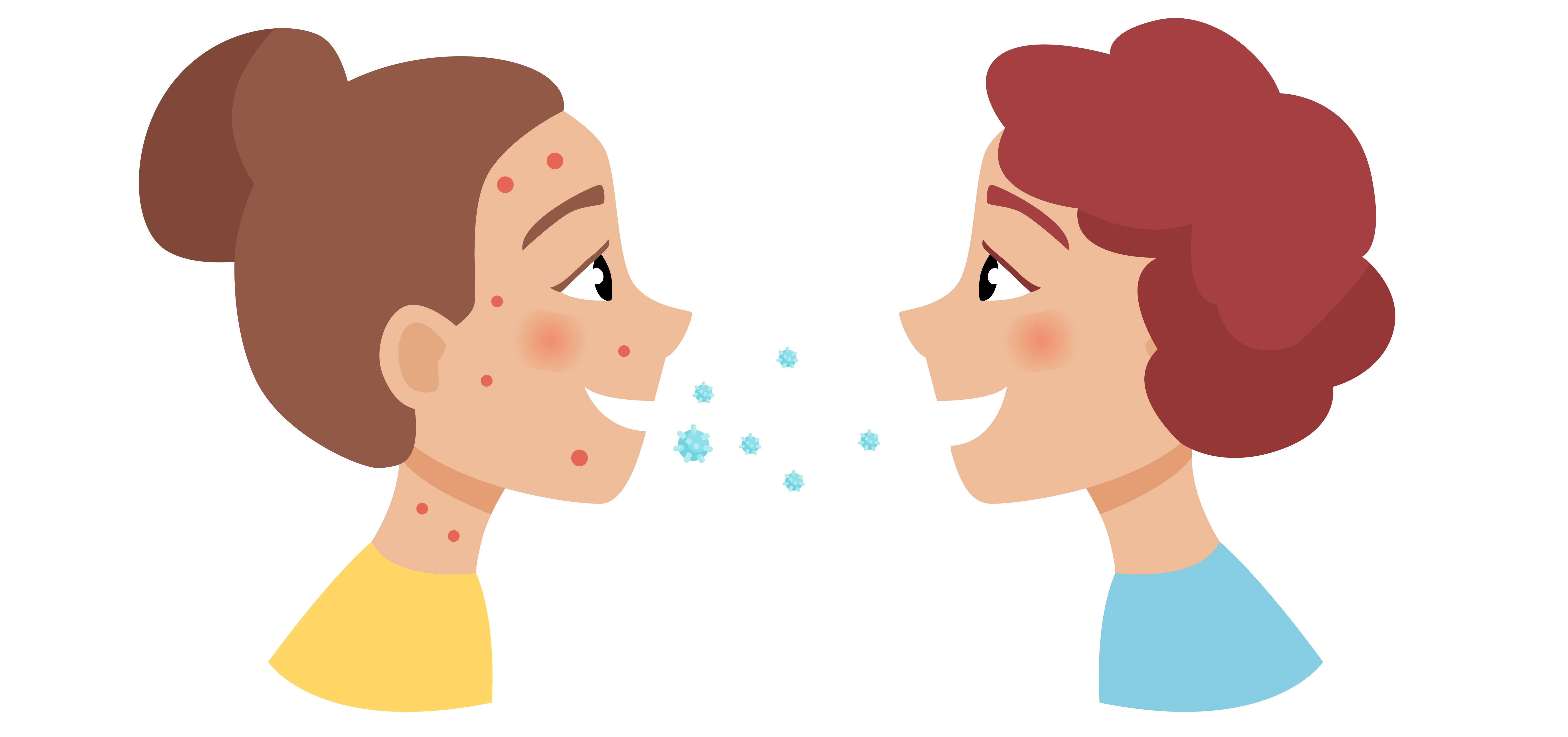
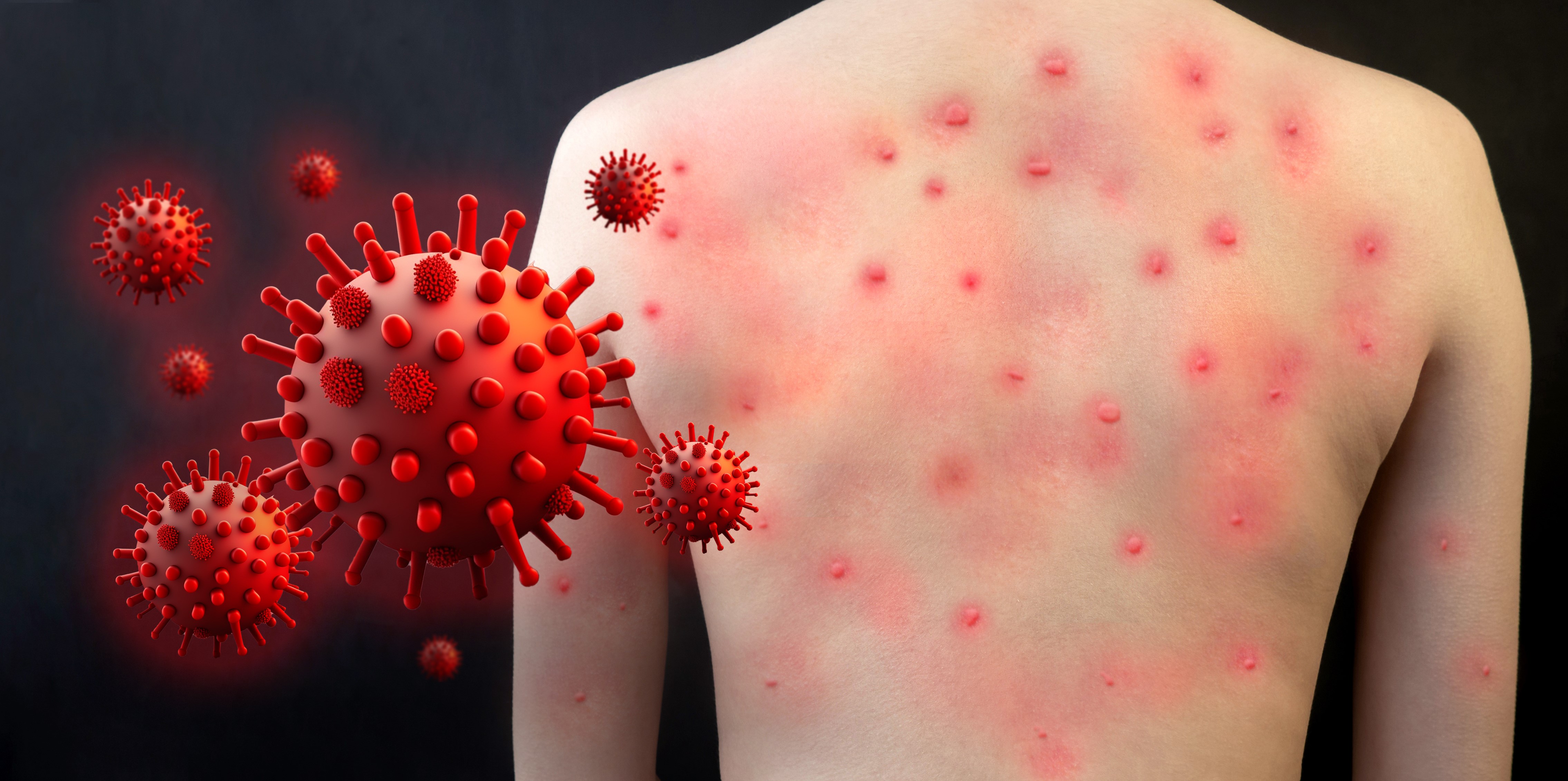
After these initial symptoms, an itchy rash with fluid-filled blisters appears throughout the body. Chickenpox blisters typically start at the chest, back, and face before spreading over the entire body. Blisters turn into scabs in 4-7 days, after other signs of illness.
Chickenpox can cause several health complications. Complications include Group A streptococcal disease (skin and soft tissue infections), encephalitis (swelling of the brain) pneumonia (lung infection), bleeding problems, sepsis (bloodstream infection) and dehydration.
Those who are more likely to have serious complications due to chickenpox are:
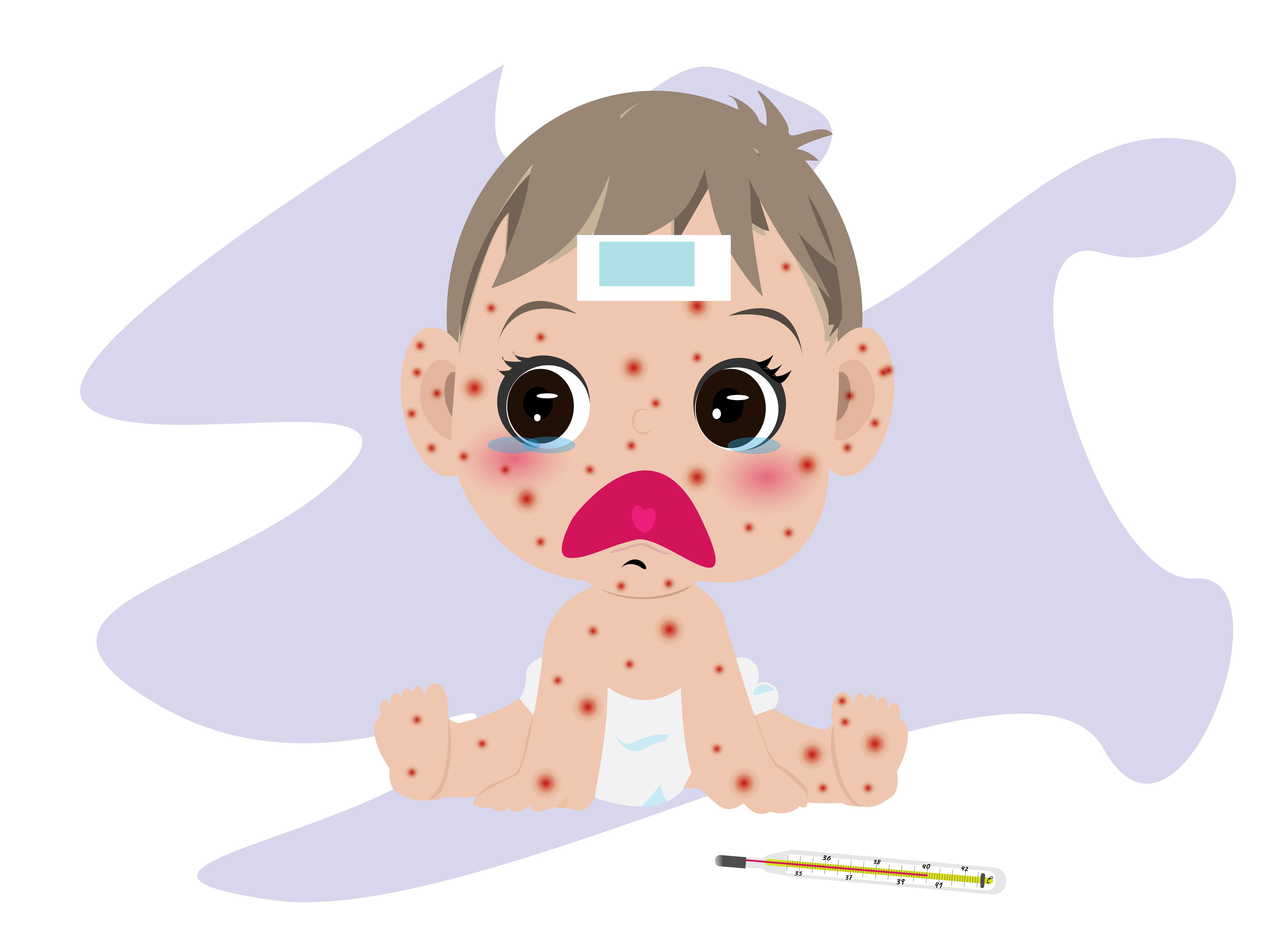
- Infants
- Adolescents
- Adults
- Pregnant People
- People with weakened immune systems
If you think you may have these symptoms, talk with your healthcare provider.